Data Governance, Smart Contracts and Privacy and Auditing: final standardisation subjects being addressed from the last pool of experts
20 November 2024
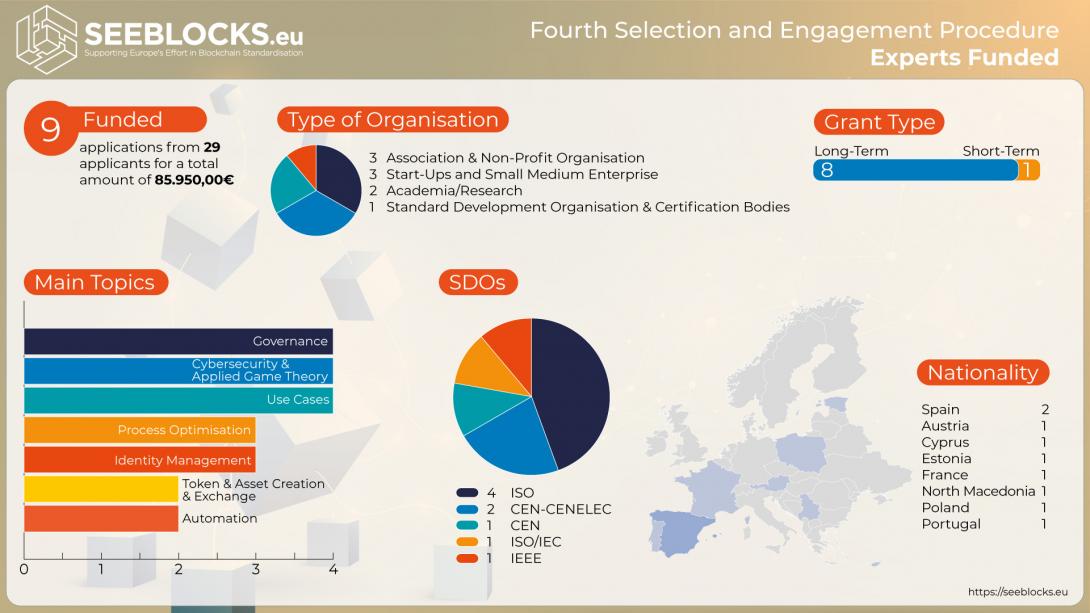
SEELBLOCKS.eu is happy to announce that our fourth and final Selection and Engagement Procedure (SEP) has been completed, with a record nine applications funded out of a total of 29 applications. Nearly 86 thousand Euros will be allocated to our group of experts to fund both new and continuing Blockchain / DLT activities. This group was the most diverse of all, with experts funded from 8 different countries: Spain, Austria, Cyprus, Estonia, France, North Macedonia, Poland, and Portugal. There was also a particularly broad range of topics addressed in this last set of expert activities, from governance to automation. Nearly all contracts awarded are long-term, reflecting the need for constant and continuing engagement in many of the standardisation activities. In the following we provide some highlights of the topics address by our SEP 4 experts.
Topics to be addressed by SEEBLOCKS.eu final cluster of experts
Good data governance is important both in the private and public sectors. But it is not always fully implemented because of perceived high costs – which in the private sector might be in monetary terms, and in the public sector might be the overwhelming bureaucratic load on personnel and citizens. But proper implementation of data governance can reduce both costs and bureaucracy. The European Data Governance Act (DGA), introduced in May 2022 and in force since August 2023, aims at establishing mechanisms to reutilise certain categories of protected data within the public sector, and could deliver considerable benefits to citizens and administrations. One of our experts is working on the design of incentives to help ensure that perceived obstacles to implementing the DGA are overcome. The work will involve the innovative use of a blockchain model inspired on the incentives model for network maintenance of public blockchains to “reimagine” new data governance solutions.
In SEP 4, work continues in the area of smart contracts. Smart contracts facilitate collaboration across industries, sectors, players, and markets and enable tracking of digital transactions and interactions. But their widespread take-up is hindered by fragmentation. Different implementations use different terminology and variations on concepts, lowering interoperability and alignment among different systems. One of our experts is focusing directly on this problem, contributing to ISO TS 18126 Taxonomy and classification for smart contracts of ISO/TC 307 WG3, Smart Contracts and their Applications. A good taxonomy and terminology form a solid foundation for ensuring interoperable smart contracts.
In fact, smart contracts have several innovative uses. One of the more intriguing applications of blockchain is in the area of robotics. We have already seen first work done by one of our experts in an earlier SEP. This work is now continuing within SEP 4, whereby the work will focus on the complexity of interaction between humans and robots, whereby blockchain can play a role in enabling smooth communication through the use of smart contracts. But once again, smooth communication depends on clearly aligned concepts and terminology, and a special focus of the expert’s work in this SEP will be ontology-based knowledge and reasoning in a robotics environment.
Yet another use of smart contracts can be in promoting environmental sustainability. The work of our experts continues also in SEP 4 on promoting environmental sustainability, both through support of blockchain / DLT of innovative applications, and through the study of environmental sustainability of the underlying blockchain/DLT technologies themselves. And one good example of this is the work of one of our experts on the development of a guidance handbook for the utilisation of Smart contracts for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations.
As noted earlier, some of the contracts awarded in SEP 4 allow our experts to continue contributing to standardisation activities that extend over a relatively long period. A good example is the work of the Joint ISO/TC 307 - ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 27 Working Group 4, where one of our experts is contributing to the ongoing development of ISO/AWI 24946 on requirements and guidance for improving, preserving, and assessing the privacy capability of DLT systems.
Speaking of privacy, a key concept in this area is Personal Identifiable Information (PII). The Working Group "CEN/CENELEC JTC19 WG3 - Personal Identifiable Information (PII) in Blockchain and DLT" is working on standardised practices for handling PII within blockchain/DLT systems, whereby one of our experts is involved in this work.
One final example concerns a topic that will become increasingly important as significant blockchain/DLT solutions begin to enter the market: the problem of certification. A well-defined, consistent procedure of auditing is the key to achieving certified, reliable systems, and certainly in applications that are mission-critical in any sector – whether it be finance, transport, health, or any of the many other sectors where it is expected that blockchain/DLT will make a major contribution. One of our experts is working on the problem of ensuring global consistency in auditing standards, to pave the way for trustworthy blockchain/DLT applications to make their expected contributions to a better society.